The Adaptive Acquisition Framework (AAF) supports the Defense Acquisition System with the objective of delivering effective, suitable, survivable, sustainable, and affordable solutions to the end-user in a timely manner. To achieve those objectives, Milestone Decision Authorities (MDAs), other Decision Authorities (DAs), and Program Managers (PMs) have broad authority to plan and manage their programs consistent with sound business practices.
Definition: The AAF supports the Defense Acquisition System with the objective of delivering effective, suitable, survivable, sustainable, and affordable solutions to the end-user in a timely manner.
The Goal of the Adaptive Acquisition Framework (AAF)
“The goal of the Adaptive Acquisition Framework is to empower innovation and common-sense decision making through the decision-making process, while also maintaining discipline in our practices and procedures.” Mr. Kevin Fahey, Assistant Secretary of Defense for Acquisition
Adaptive Acquisition Framework (AAF) Pathways
AAF acquisition pathways provide opportunities for MDAs/DAs and PMs to develop acquisition strategies and employ acquisition processes that match the characteristics of the capability being acquired. The framework has six (6) distinct acquisition pathways.
- Urgent Capability Acquisition
- Middle Tier of Acquisition
- Major Capability Acquisition
- Software Acquisition
- Defense Business System
- Acquisition of Services
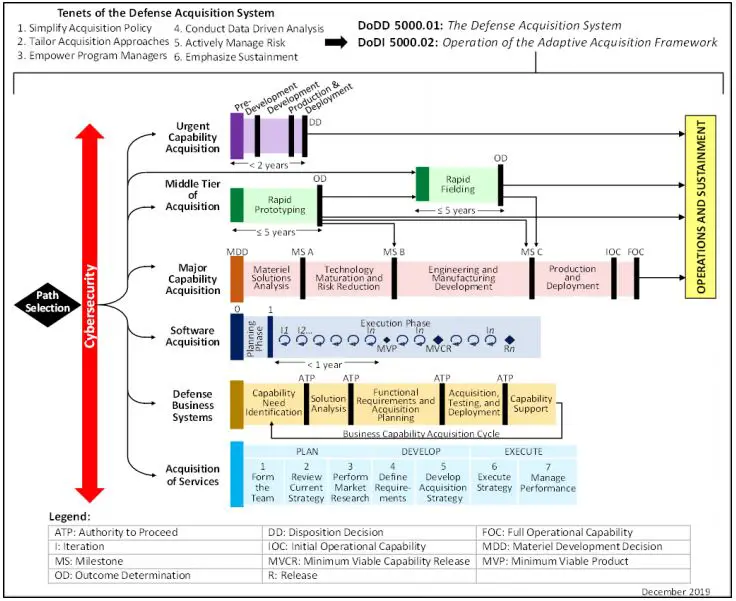
- Urgent Capability Acquisition: Needs identified by Commanders involved in an ongoing contingency operation or emergent need.
-
- Urgent Capability Acquisition
- DoD Instruction 5000.81 “Urgent Capability Acquisition”
- Fielded less than 2 years
- Joint Urgent Operational Need (JUON)
-
- Middle-Tier Acquisition: Programs that are intended to be completed in a period of 2-5 years via two acquisition pathways.
- Major Capability Acquisition (Tailorable): Execute to the standard defense acquisition model with modifications.
- Software Acquisitions: To facilitate rapid and iterative delivery of software capability to the user.
- Defense Business System: Business systems are information systems that are operated by, for, or on behalf of the DoD.
- Acquisition of Services: Acquisition of contracted services from private sector entities by or for the DoD.
Main References
Instruction: DoD Instruction 5000.02 “Operation of the Adaptive Acquisition Framework”
DAU Website: Adaptive Acquisition Framework
Utilizing a combination of Adaptive Acquisition Pathways [1]
Program Managers may leverage a combination of acquisition pathways to provide value not otherwise available through use of a single pathway. The use of multiple pathways does not affect the application of statutory thresholds otherwise applicable to the program as a whole, such as the MDAP or major system (ACAT II) thresholds unless a statute permits. PMs employing multiple pathways will:
- Define the transition points from one pathway to another pathway.
- Anticipate, develop, and coordinate the information requirements required at the new pathway entry point. Links provided in [MDID]. identify regulatory and statutory information requirements for major capability acquisition, and the statutory requirements for other pathways.
- Ensure a smooth transition.
Prototyping & Experiments
- Early Prototyping: Technology or capability that is being matured by the research laboratories.
- 10 USC 2373: Procurement for Experimental Purposes: Rapid acquisition tool for fielding and testing new capabilities
Adaptive Acquisition Pathways Test & Evaluation (T&E)
The purpose of Test & Evaluation (T&E) is to provide knowledge to assist in Risk Management that’s involved in developing, producing, operating, and sustaining systems and capabilities. The T&E process has been adapted to be part of the Adaptive Acquisition Framework by providing different T&E methods for each of the six pathways. Below is the main instruction for conducting T&E with regard to each pathway.
-
Instruction: DoD Instruction 5000.89 “Test and Evaluation”
Rapid Acquisition Contract Methods
Below is a list of contact methods that can be used to perform Rapid Acquisitions:
- Tradition Contract Types
- Other Transaction Authority (OTA)
- Indefinite Delivery Contract (IDIQ)
- Broad Agency Announcement (BAA)
- Commercial Solutions Opening (CSO)
- Undefinitized Contract Action (UCA)
- FAR Part 12 – Acquisition of Commercial Items
- FAR Part 13 – Simplified Acquisitions
Acquisition Authorities
| Method | Acquisition Authority | Decision Authority |
| Procure Defense Services | DODI 5000.74 | SAE or Designee |
| Weapons System Procurement | DODI 5000.02 | MDA |
| Section 803 | MDA equivalent to ACAT Level | |
| Section 805 | MDA equivalent to ACAT Level | |
| Rapid Middle Tier Prototyping | Section 804 – Rapid Prototyping | MDA equivalent to ACAT Level |
| Section 804 – Rapid Fielding | MDA equivalent to ACAT Level | |
| Section 806 – Weapon Component Prototyping or Technology | Selected by SAE after oversight Board Reviews | |
| Early Prototyping | DODI 3201.01 | |
| Rapid Experiments | 10 USC 2373 | |
| MDA: Milestone Decision Authority; ACAT: Acquisition Category; SAE: Service Acquisition Executive | ||
Rapid Organizations
- Joint Rapid Acquisition Cell (JRAC)
- Defense Innovation Unit (DUIx)
- Army Rapid Capabilities and Critical Technologies Office (RCCTO)
- Rapid Innovation Fund (RIF), DoD Small Business Programs
AcqNotes Tutorial
AcqLinks and References:
- DoD Instruction 5000.85 “Major Capability Acquisition” – 6 Aug 2020
- DoD Instruction 5000.81 “Urgent Capability Acquisition” – 31 Dec 19
- FY16 NDAA Section 804 “Middle Tier Acquisitions”
- DoD Instruction 5000.74 “Defense Acquisition of Services” – 5 Oct 2017
- DoD Instruction 5000.91 “Product Support for Adaptive Acquisition” – 4 Nov 2021
- [1] DoD Instruction 5000.02 ” Operation of the Adaptive Acquisition Framework“
- Department of Navy – Acquisition Gold Card Aug 21
- Website: DAU Adaptive Acquisition Framework
Updated: 2/24/2024
Rank: G4.1
