A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a tool used to define a project in discrete work elements in a Hierarchical format. It displays and defines the product, or products, to be developed and/or produced. It relates the elements of work to be accomplished to each other and to the end product. In other words, the WBS is an organized method to break down a product into subproducts at lower levels of detail. It’s used for planning, cost estimating, execution and control.
Definition: A Work Breakdown Structure is a hierarchical decomposition of work tasks that need to be performed by project team members to accomplish project goals and objectives and create the required deliverable.
Purpose of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The purpose of the WBS is to break down projects into manageable pieces, allowing for better planning, cost estimating, execution and control.
Example of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
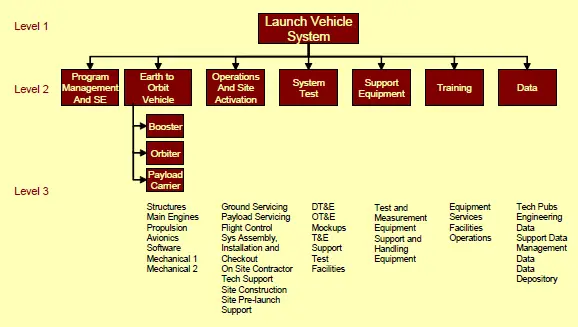
Key Takeaways About the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a tool that can be used to define and organize the total scope of a project. It is a hierarchical decomposition of the project into smaller, more manageable components. The WBS typically includes all of the work required to complete the project, including deliverables and tasks, as well as the resources needed to complete each task. Here are some key takeaways about using a WBS:
- A WBS helps to define the project scope and identify all of the work that needs to be done. This helps to ensure that nothing is left out of the project plan.
- A WBS helps to organize the project into smaller, more manageable components. This makes it easier to plan, schedule, and control the project.
- A WBS helps to identify the resources (e.g., people, materials, equipment) needed to complete each task. This helps to ensure that the necessary resources are available when they are needed.
- A WBS helps to identify the dependencies between tasks. This allows project managers to identify potential bottlenecks and make appropriate plans to address them.
- A WBS can be used to track progress and measure the completion of project deliverables. This allows project managers to monitor the project and make any necessary adjustments to keep the project on track.
AcqNotes Tutorials
Why Develop a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The WBS is a means of organizing system development activities based on system and product decompositions. It is a product-oriented family tree composed of hardware, software, services, data, and facilities, resulting from systems engineering efforts during the development and production of the system and its components, and completely defines the program. The WBS is prepared from both the physical and system architectures and identifies all necessary products and services needed for the system. This top-down structure provides a continuity of flow down for all tasks. Enough levels must be provided to define work packages for cost and schedule control purposes properly. [1]
The Benefits of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) are:
- Organizes the project deliverables and tasks
- Determines the program schedule (Integrated Master Schedule)
- Enhances communication
- Details tasks and dependencies
- Identifies all products and services a system needs
- Helps determine cost estimates
- Identify Project Phases
The Two Types of Work Breakdown Structures (WBS)
The Program Manager (PM) is usually responsible for developing an overall program WBS and initiating the development of contract WBSs for each contract in accordance with common DoD practice established in Mil-HDBK 881. The two types of WBS on a program are:
- Program WBS: A program WBS is established to provide the framework for program and technical planning, cost estimating, resource allocation, performance measurement, and status reporting. The WBS defines the total hardware, software, services, data, and facilities system and relates these elements to each other and to the end product. Program offices develop a program WBS tailoring the guidance provided in MIL-HDBK-881 and MIL-STD-881D. The WBS is also an integral part of the preparation of the Cost Analysis Requirements Description (CARD).
- Contract WBS: are part of the program WBS and relate to deliverables and tasks on a specific contract.
Initial Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Development
With the support of systems engineering, the PM develops the first three levels of the program WBS and provides contractors with guidance for lower-level WBS development. As with most standards and handbooks, the use of MIL-HDBK-881 cannot be specified as a contract requirement. Though WBS development is a systems engineering activity, it impacts costing, scheduling, budgeting professionals, and contracting officers. An integrated team representing these Stakeholders is needed to support WBS development. [1]
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Guidance (MIL-STD-881)
A WBS provides a consistent and visible framework for defense materiel items and contracts within a program. Mil-Standard 881D offers uniformity in definition and approach consistency for developing all WBS levels. Generating and applying uniform work breakdown structures improves communication in the acquisition process. It also provides direction to industry in extending contract work breakdown structures. [1]
Standard: MIL-STD-881D “DoD Standard Practice WBS for Defense Materiel Items”
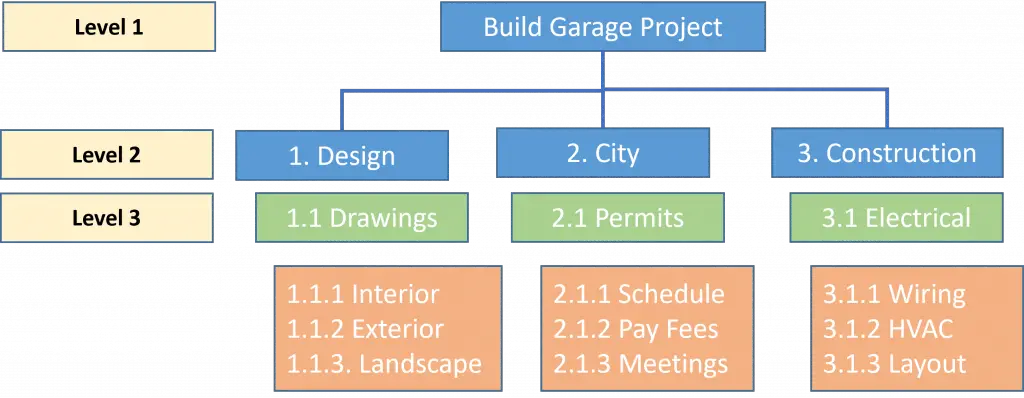
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Levels
The first three Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Levels are organized as follows:
- Level 1: Overall System
- Level 2: Major Elements (Segment)(Main Project Phases)
- Level 3: Subordinate Components (Prime Items)(Groups of Tasks)
Example: WBS Levels
How to Make a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The process of developing a WBS is straightforward but requires preparation and a clear understanding of what is required to be accomplished on a project.
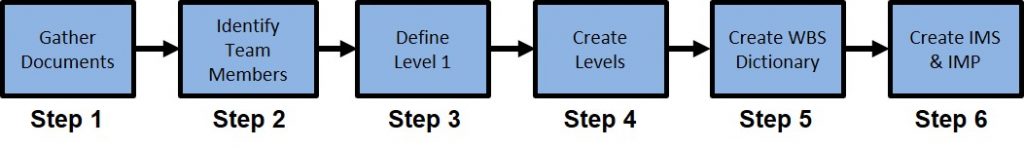
- Step 1: Gather Main Documentation: You must understand the project goals and objectives. To do this, gather the project charter, scope, objectives, and any requirements.
- Step 2: Identify Your Main Team Members: A WBS can’t be built in a vacuum. It takes a team of specialized people to know how to break their sections down into discreet parts.
- Step 3: Define WBS Level 1: This level is a summary of the deliverable that must be met to satisfy the project scope.
- Step 4: Create the WBS Levels: This is the step where you break down is WBS component into discreet events. This is the most time-consuming and important step in the process. You need to break down the work until each Element can be accomplished by a single individual or organization.
- Step 5: Create the WBS Dictionary: The Dictionary describes each work element in the WBS.
- Step 6: Create the Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) and Integrated Master Plan (IMP): This creates a complete plan of all the work that needs to be accomplished and by when.
How to Utilize a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
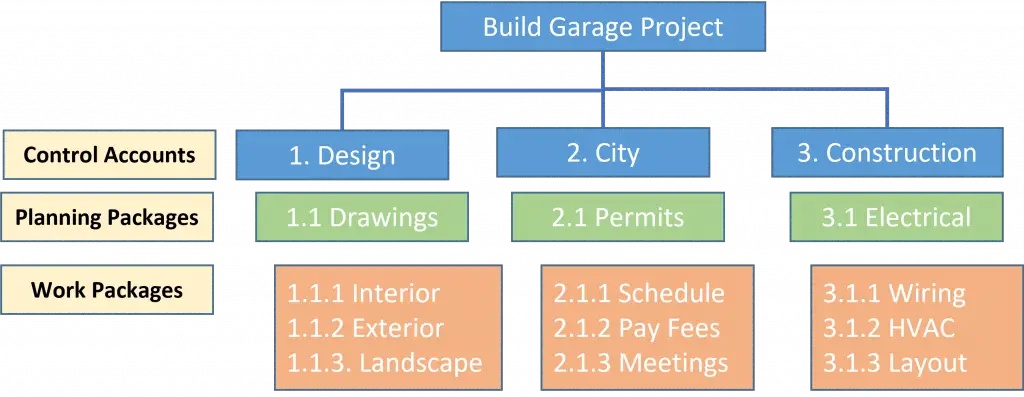
A Work Breakdown Structure is primarily used as a planning tool to help the Program Manager and project personnel plan, define and organize a project into discreet deliverables. It describes all the work that needs to be accomplished to help avoid any confusion. There are three main components of a WBS that help with defining the program. These are:
- Control Accounts: Control Account (CA) is a management control point at which budgets (resource plans) and actual costs are accumulated and compared to earned value for management control purposes. Any WBS Elements at which the project plans to monitor and report performance.
- Planning Packages: These are steps that have been created but are not fully defined yet into work packages.
- Work Packages: A work package is simply a task/activity or grouping of work and is the point at which work is planned, progress is measured, and earned value is computed. Natural subdivision of a Control Account. This information is described in the WBS Dictionary.
Example: WBS Deliverable Levels
Control Accounts in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Control Accounts are WBS Elements at which the project plans to monitor and report performance. The Control Accounts can be any Element in the WBS. To assist with the monitoring and reporting, project management information tools are used to collect, analyze and report information at any Element within the WBS.
Work Packages in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Work Package (WP) is simply a task/activity or grouping of work and is the point at which work is planned, progress is measured, and earned value is computed. It can be translated into different terms in different companies and functions. It can be a design job, a tool design package, a build-to-package, a shop order, a part number, a purchase order, or any other definable task/activity at whatever level of control is normal for program management within the company. They normally represent the lowest level of a WBS.
Work Packages Example
Work packages come in a variety of formats, but the most common format is in the WBS. Below is a WBS, and the work packages are at the bottom level.
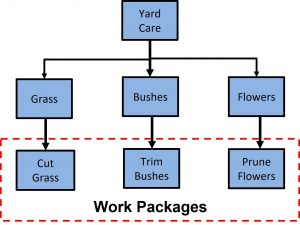
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Application Tools
There are a variety of application tools you can use in the development of a WBS. Below are some of the example types that can be used.
- Nodal Chart: A graphical representation of the deliverables in nodes.
- Flowchart: The most common WBS application
- Gantt Chart: You can show task dependencies and show project milestones.
- Spreadsheet: A WBS can be created in a spreadsheet detailing the different levels and phases in columns and rows.
- List: A simple list of deliverables. Best used for a simple WBS.
Contractor Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The contract WBS is the Government – approved WBS for program reporting purposes and includes all program elements (for example, hardware, software, services, data, or facilities), which are the contractor’s responsibility. It includes the contractor’s discretionary extension to lower levels, in accordance with Government direction and the contract Statement of Work (SOW).
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Dictionary
The WBS Dictionary is a document that describes each element work package in a project component of the WBS. These elements can include milestones, deliverables, activities, scope, resources, costs, and quality. The main purpose of the WBS dictionary is to define and communicate the work in more detail to help those working on an element or work package understand what needs to be done.
AcqLinks and References:
- [1] SMC Systems Engineering Handbook
- MIL-Hand Book-881: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- MIL-STD-881D “DoD Standard Practice Work Breakdown Structure for Defense Materiel Items” – April 18
- Old: MIL-STD-881C DoD Standard Practice Work Breakdown Structure for Defense Materiel Items – 3 Oct 11
Updated: 1/1/2023
Rank: G27.3