The Software Development Plan (SDP) describes a developer’s plans for conducting a software development effort. The SDP provides the acquirer insight and a tool for monitoring the processes to be followed for software development. It also details methods and approaches for each activity, organization, and resource. It helps ensure that software development is done systematically and structured, increasing the chances that the project will be finished successfully.
Definition: A Software Development Plan (SDP) is a document that outlines the overall approach and strategies for developing a software project. It serves as a roadmap that guides the software development team throughout the project’s lifecycle, providing a framework for planning, executing, and controlling the development process.
Purpose of a Software Development Plan (SDP)
The purpose of the SDP is to communicate to team members and stakeholders the approach to be taken when developing software on a program and how a Program Manager will utilize direct resources.
Objectives of a Software Development Plan (SDP)
The objective of any SDP is to provide a framework where team members on a software project have a clear understanding of the software they are developing and the problems they are trying to solve. An SDP answers the following questions:
- What problems are being addressed and solved?
- What are the main tasks of development?
- What software development approach will be utilized?
- What are the key functions of the software?
- What is the overall schedule of development and critical path?
- What is the order of development?
- Who is in charge?
- What are the team responsibilities (Responsibility Assignment Matrix)
- How is the project divided up?
- How is quality control going to be implemented and measured?
AcqNotes Tutorial
How to Develop a Software Development Plan (SDP)
The SDP should be developed in the contractor‘s preferred format and should document all processes applicable to the system to be acquired at a level of detail sufficient to allow the use of the SDP as the full guidance for the developers. It should reference specific standards, methods, tools, actions, reuse strategies, and responsibilities associated with the development and qualification of all requirements, including safety and security. At a minimum, a well-prepared SDP should address the following topics:
-
The scope of work that is required to be executed in the development
-
Timeline of all the tasks required for completion
-
Project deadlines
-
The sequence of task completion and their levels of priority
-
Task assignment and responsibilities
-
Additional planning for budget, schedule, risk management, and quality control
Software Development Plan (SDP) Steps
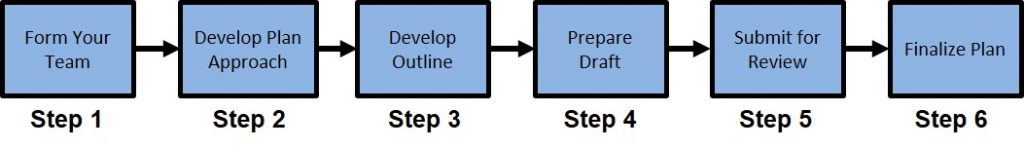
There are six steps associated with the development of an SDP. These six steps are:
- Step 1: Form Your Team: Gather the subject matter experts you will need to develop the SDP.
- Step 2: Develop Plan Approach: Figure out how you are going to write the plan and who is responsible for each section.
- Step 3: Develop Outline: Start with an outline or a template. This step needs to ensure all required information is addressed in the SDP.
- Step 4: Prepare Draft: Write the first draft of the SDP.
- Step 5: Submit for Review: Submit the first draft to all team members who will utilize the plan for their feedback.
- Step 6: Finalize SDP: Submit the final SDP to the team
Software Development Plan (SDP) Template
Using a template is the best place to start when developing your SDP. The template will provide a starting point in the creation of the plan and will make sure you address all the main objectives in an SDP that need to be covered. Below is a good template that you can utilize.
Template: Software Development Plan
Outline of a Software Development Plan (SDP)
The SDP usually has the following sections:
- Introduction: This part gives an overview of the software project, including its purpose, goals, and scope. It could also give any past information or context that is important.
- Project Organization: The SDP explains how the project team is set up, including the roles and duties of each team member, who they report to, and how they can talk to each other. It names the most important people and explains how they will be involved in the growth process.
- Project Schedule: This part shows the software development project’s major milestones, deliverables, and deadlines. It might use Gantt charts or other planning tools to show how long the job will take.
- Resources: The SDP lists the resources the project will need, such as people, tools, software, and places to work. It says how these resources will be used and may include plans for buying, training, and setting up any facilities that will be needed.
- Risk management: This part deals with possible risks and unknowns that could affect the project’s success. It includes an analysis of risks, their possible effects, and ways to deal with them. Plans for risk management might also include backup plans and ways to deal with things that don’t go as planned.
- Development Methodology: The SDP describes the method or plans for making software that will be used for the whole project. It may be said that agile methods like Scrum or more standard methods like Waterfall will be used. The chosen methodology decides how tasks are set up, how work is tracked, and how the software’s quality is ensured.
- Quality Assurance: This part describes the plans and activities that will be used to make sure that the software being made is of high quality. It could include plans for code reviews, testing processes, documentation standards, and quality metrics. It may also discuss how problems will be found, handled, and fixed.
- Configuration Management: The SDP describes the methods and tools for managing software configurations, such as version control, build management, and release management. It sets rules for branches, merging, and keeping a stable codebase under control.
- Documents: The SDP says what kind of documents the software project needs. It may have plans for user manuals, technical documentation, design documents, and other things that must be made during the creation process.
- Project Monitoring and Control: This part explains how to track the progress of a project, keep track of performance metrics, and keep changes under control. It could include procedures for change management, progress meetings, and regular reports on the project’s state.
Software Development Plan (SDP) Required Information
The SDP should contain the following information, as applicable: [1]
- Plan introduction and overview.
- Purpose, scope, and objectives.
- Assumptions and constraints.
- Relationship to other program plans.
- Referenced Documents.
- Identification of all software and software products to which the SDP applies.
- Definition of terms and acronyms.
- System overview, including system and software architecture.
- Overview of required work, including:
- Requirements and constraints on the system and software to be developed.
- Software products and related deliverables.
- Requirements and constraints on project documentation.
- The program/acquisition strategy, resources, and schedules
- Additional requirements and constraints include project security, privacy, methods, standards, and hardware and software development interdependencies.
- Known software-specific risks.
- Project organization and resources:
- Plans for performing general software development activities, including:
- Software development processes.
- Software Development Approaches
- Software development methods.
- Software development standards
- Reusable software products and Commercial-off-the-Shelf (COTS)
- Software types/categories (i.e., operational software, test software, support equipment software) and associated processes, controls, and documentation.
- Handling of critical requirements (such as safety, security, and information assurance).
- Incremental development approach, planning, and management/oversight.
- Establishing the system/software engineering environment.
- Computer resources utilization and reserve capacity/growth management.
- Software-related development processes, including:
- Overall development methodology.
- Prototyping and simulations.
- System requirements analysis and design, including requirements definition and allocation
- Software requirements analysis.
- Software preliminary and detailed design.
- Software unit integration and testing.
- Software component integration and testing.
- Supporting processes and information, including:
- Software risk management.
- Approach to requirements traceability.
Key Questions the Software Development Plan (SDP) Needs to Communicate
- What kinds of problems is the software project trying to solve?
- Which jobs are most important?
- What kinds of tools does the project call for?
- How long will it take to finish the project/sprints?
- What are the key dates, deliverables, goals, and dependencies?
- Who is taking part in the project?
- What are the roles of each person on the team?
- How do you measure the quality?
Avoid These 10 Key Mistakes When Writing a Software Development Plan (SDP)
When writing a plan for making software, there are a few common mistakes that you should try to avoid. Here are some important mistakes to avoid:
- Inadequate Requirements Analysis: If you don’t fully understand and write down the software project’s needs, it could cause big problems in the future. It’s important to involve stakeholders, collect requirements, and ensure they are clear, full, and reasonable.
- Setting unrealistic timeframes and deadlines: Setting unrealistic timeframes and deadlines can add extra stress and lead to rushed development, lower quality, and a higher chance of making mistakes. It is important to think carefully about the job’s size and complexity and to set realistic and doable deadlines.
- Not Including Stakeholders: If you don’t include key stakeholders in the planning process, the project goals and the stakeholders’ standards might not match up. It is important to involve stakeholders, get their feedback, and make sure the plan meets their goals.
- Not enough risk management: If you don’t find and deal with possible risks, your project could be delayed, go over price, or have quality problems. Risk management should be a big part of the plan. This includes finding risks, assessing them, developing ways to deal with them, and making backup plans.
- Bad Resource Allocation: Badly allocating resources like people, gear, or software tools can cause inefficiency, delays, and quality problems. It is very important to carefully evaluate the project’s needs and ensure enough resources are set aside to meet them.
- Lack of flexibility: Plans that are too set in stone and don’t account for changes or unplanned events can make it hard to adapt to changing project needs. It is important to make the plan flexible so that it can be changed and improved as the project goes on.
- Ignoring Quality Assurance: If you don’t pay enough attention to quality assurance processes and activities, software bugs, bad user experiences, and more upkeep work can happen. The plan should have a full strategy for testing, code reviews, documents, and measuring quality.
- Bad Communication: Misunderstandings, delays, and conflicts can happen when people on the development team or with clients don’t talk to each other well. The plan should include clear ways to communicate, regular ways to report, and good ways to work together.
- Not keeping good documentation: If you don’t keep good documentation during the development process, it can be hard to understand, manage, and scale the software in the future. The plan should include rules and standards for documentation to ensure that important artifacts are made and kept up to date.
- Failing to keep an eye on the project and make changes as needed. If you don’t monitor how the project is going, track metrics, and change the plan as needed, you could miss deadlines and have a bad result. To keep the project on track, it’s important to look at the plan and make changes based on comments, progress, and changes.
AcqLinks and References:
- [1] USAF Weapon Systems Software Management Guidebook – Appendix I
- Mil-STD-498 “Software Development and Documentation” – 5 Dec 1994
- Mil-STD-498 “Application and Reference Guidebook” – 3 Jan 1996
- Software Development Plan Information Outline
- Template: Software Development Plan – SPAWAR
Updated: 2/9/2024
Rank: G1.6
