The Continuous Improvement Process (CIP) is an ongoing effort to enhance the quality of products, services, or processes through small changes. It involves implementing minor iterative modifications that accumulate into substantial outcomes by intentionally examining existing procedures. The six-step systematic approach entails planning, sequencing, and implementing improvement activities based on data. It further expands on the Shewhart Cycle, which consists of the steps: Plan, Do, Study, Act. The CIP makes the improvement process easier to understand using a standard set of words and methods.
Definition: Continuous improvement is the act of continually looking to improve upon a process, product, or service through small incremental steps. It is a organized method to continuous identify, define, implement, measure, and analyze the effectiveness of change.
Purpose of a Continuous Improvement Process (CIP)
The purpose of the continuous improvement process is to improve the performance, efficiency, and effectiveness of a company over time. Finding, studying, and putting into action ways to make processes, products, or services better in order to boost quality, productivity, and customer satisfaction is what this iterative method is all about.
Benefits of a Continuous Improvement Process (CIP)
Implementing a Continuous Improvement Process in an organization should be standard practice now. Studies have shown the main benefits of a CIP are:
- Increase productivity: Increases productivity by finding and getting rid of waste, improving processes, and making the best use of resources, which means more work can be done with the same or fewer resources.
- Better teamwork and morale: create an environment where people are willing to work together and take responsibility. This makes everyone feel valued for their part in improving processes and reaching shared goals, which leads to better teamwork and higher morale.
- Greater agility: makes businesses more flexible and responsive, which helps them respond quickly to changing situations. This flexibility lets them quickly adapt to changes in the market and in what customers want.
- Less waste: Using methods for ongoing improvement, like Lean principles, can help reduce waste by finding and getting rid of activities that don’t add value, cutting down on unnecessary inventory, and making the best use of resources, which leads to better resource utilization.
- More efficiency: The goal of continuous improvement is to improve and streamline processes, which makes them more efficient by eliminating bottlenecks, making routines smoother, and making operations run more smoothly overall.
- Increase customer satisfaction: makes sure that goods and services meet or go beyond what customers expect by constantly improving processes and quickly fixing problems. This leads to better quality, dependability, and overall customer satisfaction.
- Increase in profit: has a good effect on the bottom line by increasing customer satisfaction, making the business more productive, and reducing waste. This leads to higher profits and long-term business growth.
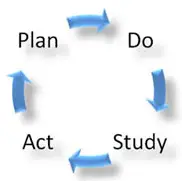
Phases of the Shewhart Cycle Continuous Improvement Process (CIP)
The Shewhart Cycle is one of the methods that can be used by an organization for continuous improvement and is central to understanding project and program life cycles. (See Below for more Methods) There are four phases associated with the CIP utilizing the Shewhart Cycle:
- Phase 1 “Plan”: Plan for change and identify improvement opportunities.
- Phase 2 “Do”: Implement changes identified.
- Phase 3 “Study”: Check to determine if the change had the desired outcome.
- Phase 4 “Act”: If successful, implement it across the organization and process.
The Six (6) Steps of the Continuous Improvement Process (CIP)
Organizations use the dynamic and methodical continuous improvement process to improve productivity, output, and overall performance. The fundamental components of the approach are the Six Steps, a methodical framework created to lead teams through the process of finding, evaluating, and introducing process changes. Most of the CIP methods follow the six basic steps below in their execution.
- Step 1: Identify Improvement Opportunity: Select the appropriate process for improvement.
- Evaluate Process:
- Select a challenge/problem
- Step 2: Analyze: Identify and verify the root cause(s).
- Step 3: Take Action: Plan and implement actions that correct the root cause(s).
- Step 4: Study Results: Confirm the actions taken to achieve the target.
- Step 5: Standardize Solution: Ensure the improved level of performance is maintained.
- Step 6: Plan for the Future:
- Plan what is to be done with any remaining problems
- Evaluate the team’s effectiveness
- Set a target for improvement
Common Methods of Continuous Improvement
There are a few methods for continuous improvement. Each method helps program personnel improve products, services, or processes by reducing variation, defects, and cycle times.
- Shewhart Cycle (PDCA): Developed by Walter A. Shewhart, the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is a systematic approach to continuous improvement. It involves planning a change, implementing it, observing the results, and then taking corrective actions based on those observations. This iterative process enhances efficiency and quality by continuously refining processes.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology to minimize defects and process variations to achieve near-perfect results. It employs statistical tools and techniques to improve process performance systematically. By focusing on customer requirements and utilizing the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework, Six Sigma aims to drive continuous improvement and increase overall organizational effectiveness.
- Kanban: a visual management system designed to optimize workflow and minimize waste. Using visual cues such as cards or boards, Kanban helps teams visualize work, limit work in progress, and continuously improve efficiency by identifying bottlenecks and optimizing the flow of tasks through the system.
- Kaizen: approach emphasizes tiny, frequently simple-to-implement adjustments because it recognizes that even small improvements can have a big impact on other parts of the company.
- Lean Manufacturing: emphasizes the elimination of waste and continuously improving processes. It involves streamlining operations, reducing inventory, and focusing on customer value. By embracing principles such as Just-In-Time production and continuous flow, Lean Manufacturing aims to enhance productivity and minimize resource utilization.
- Theory of Constraints (TOC): focuses on identifying and alleviating constraints within a system to improve overall efficiency. It advocates identifying the “weakest link” in a process and systematically addressing it to enhance throughput. TOC aims to maximize the performance of a system by removing constraints and optimizing resource utilization.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): a comprehensive approach to continuous improvement that involves all members of an organization in a commitment to delivering high-quality products and services. TQM emphasizes customer satisfaction, employee involvement, and a continuous focus on process improvement. By fostering a culture of quality throughout the organization, TQM aims to enhance customer loyalty and organizational performance.
Continuous Improvement Process Tutorial
The Best Time to Start a Continuous Improvement Process (CIP)
There is no bad time to start using a continuous improvement process, but the sooner, the better. Below is a list of the times I believe a CIP should be implemented:
- Beginning of a new project
- Development of processes and procedures
- Developing a new or improved product, or service
- Planning data collection and analysis
- Implementing any change to a process
- Whenever a failure occurs
Tools that can be used to help with the Continual Improvement Process (CIP) are:
- Benchmarking
- Force Field Analysis
- Flowcharts
- Affinity Diagram
- Delphi Technique
- Pareto Chart
- Cause and Effect Diagram
- Scatter Diagram
- Check Sheet
- Control Chart
- Process Capability Index and Ratio
- ISO 14000
Lessons Learned from the Continuous Improvement Process (CIP)
The following are some of the most important lessons that can be learned by utilizing a continuous improvement process:
- Start small and improve one part at a time: It’s important to start small and work on one part of a project or process at a time. By doing this, you can take small steps forward and gain speed.
- Don’t forget your team: For continuous improvement to work well takes a team. Include your team in figuring out where the problems are and how to fix them. This will get people involved and make sure that the changes you make will last.
- Measure and keep track of your progress: to see if your efforts for continuous improvement are working or not. Then you can make any necessary changes to see if your changes had the effect you wanted.
- Be flexible: To keep improving, you must be willing to change and try new things. Be open to new ideas and ways of doing things, even if they seem strange.
- Learn: Because continuous improvement is an iterative process, you should be willing to try new ideas and learn from your mistakes. Take advantage of the opportunity to grow and learn as you go.
AcqLinks and References:
- [1] Defense AT&L: Continuous Process Improvement within the DoD by David Pearson July 2007
- DoD Directive 5010.42 “DoD-Wide Continuous Process Improvement (CPI) Lean Six Sigma (LSS)” – 15 May 2008
- Air Force Instruction 38-401 “Continuous Improvement Process” – Aug 2019
- Manual: DCMA Manual 4502-05 Continuous Process Improvement – Dec 2020
- Website: DoD Chief Management Office: Continuous Improvement Process
Updated: 2/5/2024
Rank: G8.4
