The Department of Defense (DoD) Acquisition system is directed by DoD Instruction 5000.85 “Major Capability Acquisitions”. This instruction provides the policies and principles that govern the defense acquisition system and the phases that form the foundation for all DoD programs. It also identifies the specific statutory and regulatory reports and other information requirements for each phase and Milestone. The DoD calls the system an event-based process where a program goes through a series of phases, milestones, and reviews from beginning to end. Each milestone is the culmination of a phase where it’s determined if a program will process into the next phase.
Defense Acquisition Process Phases
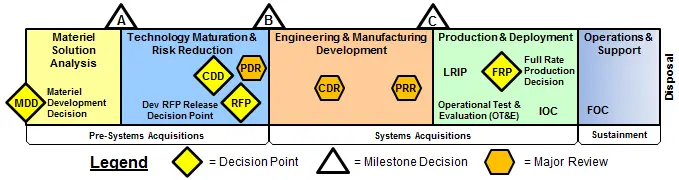
The defense acquisition process encompasses five separate phases in the development of a system. The phases are enumerated and depicted below in the graphic of the acquisition process.
- Materiel Solutional Analysis (MSA)
- Technology Maturation & Risk Reduction (TMRR)
- Engineering & Manufacturing Development (EMD)
- Production & Deployment (PD)
- Operations & Support (O&S)
Materiel Solutions Analysis (MSA) Phase
The purpose of MSA Phase A is to analyze all potential material solutions for an identified need stated in an Initial Capabilities Document (ICD). The phases consist of an Analysis of Alternatives (AoA) and Material Solution Analysis activities to include measures of effectiveness, cost estimates, schedule, the concept of operations, and risk. The goal of this phase is to recommend possible solutions for further exploration in the Technology Maturation & Risk Reduction (TMRR) Phase.
Technology Maturation & Risk Reduction (TMRR) Phase
The purpose of the TMRR phase is to reduce technology risks and to determine the appropriate set of technologies to be integrated into a future system that satisfies the needs of an ICD. This phase will consist of risk reduction, cost estimations, and programmatic activities. The goal of this phase is to reduce the technology risk to an acceptable level, have a defined set of requirements in a Capability Development Document (CDD), and a preliminary acquisition strategy to start an official program in the next phase.
Engineering & Manufacturing Development (EMD) Phase
Phase EMD is the start of an official program. The purpose of this phase is the development of a capability. This phase starts after a Milestone B review and consists of two efforts, Integrated System Design (ISD) and System Capability and Manufacturing Process Demonstration (SC&MP). It also contains a Critical Design Review (CDR) Assessment at the conclusion of the ISD effort. The goal of this phase is to complete the engineering development of a capability or system and proceed into production and development.
Production and Development (PD) Phase
The purpose of the PD Phase is to achieve an operational capability that satisfies the user’s and mission needs. This phase consists of two efforts: Low-Rate Initial Production (LRIP) and Full-Rate Production Decision Review (FRPDR). The phase will also include operational testing of the capability to determine its effectiveness.
Operations and Support (OS) Phase
The purpose of the OS Phase is Life-Cycle Sustainment and Disposal. This phase is initiated by the deployment of the first fielded system of a program. The Life-Cycle Sustainment efforts overlap the FRPDR effort of the Production and Development Phase. The phase ends with the final disposal of a system.
AcqNotes Tutorial
AcqTips:
- See Defense Acquisition Life Cycle Wall Chart for more information on what needs to be accomplished in each phase
AcqLinks and References:
- DoD Instruction 5000.85 “Major Capability Acquisitions”
- DoD Directive 5000.01 “Defense Acquisition System”
- DoD Instruction 5000.02 “Operation of the Defense Acquisition System”
- Defense Acquisition Life Cycle Wall Chart – 18 Apr 2017
- DoD Integrated Product Support Implementation Roadmap
- DTM 09-027: Implementation of the Weapons System Acquisition Reform Act of 2009 (WSARA)
Updated: 3/18/2024
Rank: G1.5
