 Risk analysis is the activity of examining each identified risk to refine the description of the risk, isolate the cause, determine the effects, aid in setting risk mitigation priorities. It refines each risk in terms of its likelihood, its consequence, and its relationship to other risk areas or processes. The analysis begins with a detailed study of the risks that have been identified. The frequently used term “Risk Assessment” includes the distinct activities of Risk Identification and risk analysis. [1]
Risk analysis is the activity of examining each identified risk to refine the description of the risk, isolate the cause, determine the effects, aid in setting risk mitigation priorities. It refines each risk in terms of its likelihood, its consequence, and its relationship to other risk areas or processes. The analysis begins with a detailed study of the risks that have been identified. The frequently used term “Risk Assessment” includes the distinct activities of Risk Identification and risk analysis. [1]
Definition: Risk analysis is the process of assessing the likelihood of an adverse event occurring within a program, project, or organization.
Risk Management Overview
Risk management is a continuous process that is accomplished throughout the life cycle of a system and should begin at the earliest stages of program planning. It is an organized methodology for continuously identifying and measuring the unknowns; developing mitigation options; selecting, planning, and implementing appropriate risk mitigations; and tracking the implementation to ensure successful risk reduction.
Risk Management Process
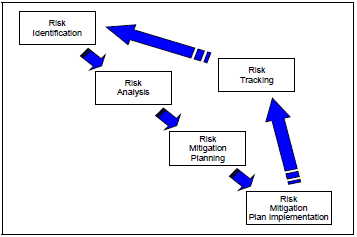
The Risk Analysis is one step in the risk management process that includes the following continuous key activities:
- Risk Identification
- Risk Analysis
- Risk Mitigation Planning
- Risk Mitigation Plan Implementation
- Risk Tracking
Risk Analysis Objective
The objective is to gather enough information about future risks to judge the root causes, the likelihood, and the consequences if the risk occurs.
Risk Analysis Intent
The intent of Risk Analysis is to understand the level of a risk(s) by:
- Considering the likelihood of the root cause occurrence;
- Identifying the possible consequences in terms of performance, schedule, and cost; and
- Identifying the risk level using the Risk Reporting Matrix.
Risk Analysis Tasks: [1]
- Develop probability and consequence scales by allocating consequence thresholds against the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) or other breakouts;
- Assign a probability of occurrence to each risk using the criteria in the Risk Reporting Matrix.
- Determine consequence in terms of Performance, Schedule, and/or Cost impact using defined criteria;
- Document the results in the program Risk Register.
Risk = Rate of occurrence * The impact of the event
Risk Analysis Performance Considerations [1]
Is there an impact to technical performance and to what level? If so, this risk has a performance consequence. These risks generally have associated schedule and cost impacts, but should be carried as a performance risk.
- Operational (e.g., Initial Capabilities Document (ICD), Capability Development Document (CDD), Capability Production Document (CPD), threats, suitability, effectiveness).
- Technical (e.g., SEP, Technology Readiness Levels, specifications, TEMP, technical baselines, standards, materiel readiness )
- Management (e.g., organization, staffing levels, personnel qualifications/experience, funding, management processes, planning, documentation, logistics)
Risk Analysis Schedule Considerations [1]
Is there an impact to schedule performance and to what level? If the risk does not have a first order performance impact, then ask this question. If the risk does impact the critical path, then it impacts both schedule and cost, but should be carried as a schedule risk.
- Evaluating baseline schedule inputs (durations and network logic);
- Incorporating technical assessment and schedule uncertainty inputs to the program schedule model;
- Evaluating impacts to program schedule based on technical team assessment;
- Performing schedule analysis on the program Integrated Master Schedule (IMS), incorporating the potential impact from all contract schedules and associated government activities;
- Quantifying schedule excursions reflecting the effects of cost risks, including resource constraints;
Risk Analysis Cost (C) Considerations [1]
Does the risk only impact life-cycle cost? If so, with no performance or schedule impacts, the risk is a cost risk, and may impact estimates and assessments such as:
- Building on technical and schedule assessment results;
- Translating performance and schedule risks into life-cycle cost;
- Deriving life-cycle cost estimates by integrating technical assessment and schedule risk impacts on resources;
- Establishing budgetary requirements consistent with fiscal year planning;
- Determining if the adequacy and phasing of funding supports the technical and acquisition approaches;
- Providing program Life-Cycle Cost (LCC) excursions from near-term budget execution impacts and external budget changes and constraints; and
- Documenting the cost basis and risk impacts.
AcqTips:
- For more detailed explanation on risk, visit the DoD Risk Issue and Opportunity Management Guidance for Defense Acquisition Programs – June 2015.
AcqLinks and References:
- DoD Risk, Issue, and Opportunity Management Guide for Defense Acquisitions- Jan 2017
- [1] DoD Risk Management Guidebook – Section 4.0 – Aug 06 (Outdated)
- Template: Risk Management Plan
- Template: Project Rick Management Template
Updated: 7/18/2021
Rank: G41.6
