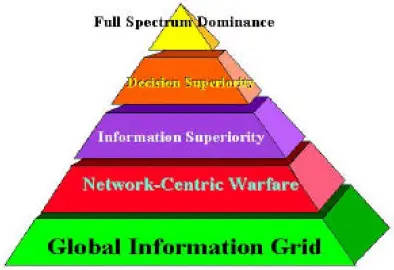
Information Superiority is the operational advantage derived from the ability to collect, process, and disseminate an uninterrupted flow of information while exploiting or denying an adversary’s ability to do the same.
The Department of Defense (DoD) strategic vision for the 21st century is to ensure that U.S. forces have information superiority in every mission area and to provide all of DoD’s customers with assured and secure connectivity on a protected global network. It’s the backbone of the Revolution in Military Affairs and provides comprehensive knowledge of the status and intentions of both adversary and friendly forces across the air, land, sea, and space components of the battlespace. Access to, use of, and control of space are fundamental to this strategy, including reliable and affordable transport of payloads and an ability to protect assets in orbit and on the ground. Space systems are an integral part of the deterrent posture of the armed forces, and they confer a decisive advantage upon U.S. and friendly forces.
Information Superiority is a key component to the Global Information Grid (GIG). The GIG includes all owned and leased communications and computing systems and services, software (including applications), data, security services, and other associated services necessary to achieve Information Superiority.
Essential elements of Information Superiority include:
- Command and Control (C2)
- Military Communications
- Computers
- Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (C4ISR)
- Information Operations (IO)
Army Vision 2010“We must have information superiority: the capability to collect, process, and disseminate an uninterrupted flow of information while exploiting or denying an adversary’s ability to do the same”
DoD Directive 5000.01, “The Defense Acquisition System” E1.1.10 “Information Superiority: Acquisition managers shall provide U.S. Forces with systems and families of systems that are secure, reliable, interoperable, compatible with the electromagnetic spectrum environment, and able to communicate across a universal information technology infrastructure, including NSS, consisting of data, information, processes, organizational interactions, skills, analytical expertise, other systems, networks, and information exchange capabilities.”
AcqLinks and References:
- Defense Acquisition Guidebook ( DAG) – Chapter 7.5
- Joint Publication 3-13 “Information Operations” – 13 Feb 2006
- Article: Information Superiority in the Pacific Fleet by Archie Clemis
- Website: Chapter 7 “Information Superiority and Space”
- Website: Army Vision 2010 Information Superiority
- Presentation: Information Superiority by Dr. David Alberts
Updated: 7/20/2017