Cyberspace is the global domain within the information environment consisting of the interdependent network of information technology infrastructures, including the Internet, telecommunications networks, computer systems, and embedded processors and controllers. Among many other things, cyberspace enables users to conduct business, communicate, socialize, connect, exchange ideas, play games, participate in social forums, and share information. Cyberspace can be viewed as three layers (physical, logical, and social) made up of five components (geographic, physical network, logical network, cyber persona, and persona).
Definition: “Cyberspace is a global domain within the information environment consisting of the interdependent network of information systems infrastructures including the Internet, telecommunications networks, computer systems, and embedded processors and controllers.” (National Institute of Standards and Technology)
Understanding Cyberspace
Understanding cyberspace is critical in today’s connected world because it has a widespread impact on almost every element of modern life. From intimate relationships to global commerce, cyberspace is the foundation of our digital civilization. Here’s why understanding its dynamics is important:
- Technology Advancement: Cyberspace refers to the global network of information technology infrastructures, telecommunication networks, and computer processing systems. Understanding its complexity is critical to technical advancement and innovation. Businesses rely on cyberspace to create and launch new products and services, which fuels economic growth and competition.
- Implications for Security: As cyberspace has grown rapidly, so have security risks. Cyberattacks on individuals, corporations, and even nations have become widespread. Understanding cyberspace is critical for creating successful cybersecurity strategies to combat threats like hacking, malware, and data breaches. Governments and armed forces must know cyberspace to protect national security interests and key infrastructure.
- Information Exchange: Cyberspace provides a vast platform for information sharing and dissemination. It allows people to access a variety of information, connect with others worldwide, and participate in online communities. Understanding cyberspace enables people to navigate the digital realm responsibly, separating reputable sources from misinformation or disinformation.
- Worldwide Communication: Cyberspace transcends geographical borders, allowing for worldwide communication and collaboration. Businesses use cyberspace to extend their markets, form international relationships, and streamline operations. Governments use cyberspace to conduct diplomatic interactions, disaster response, and humanitarian relief operations. Understanding cyberspace contributes to a more linked and cooperative global community.
- Economic Development: Cyberspace is important in fostering economic growth and wealth. Businesses may access clients worldwide using e-commerce platforms promoting global trade and commerce. Cloud computing and artificial intelligence are examples of cyberspace-powered digital technologies that improve productivity and efficiency across industries. To capitalize on cyberspace’s potential for long-term economic growth, politicians and corporate leaders must first understand it.
DoD Strategic Cyberspace Initiative
Below is a list of the five (5) DoD Strategic Initiatives for Cyberspace: [1]
- Strategic Initiative 1: Treat cyberspace as an operational domain to organize, train, and equip so that DoD can take full advantage of cyberspace’s potential
- Strategic Initiative 2: Employ new defense operating concepts to protect DoD networks and systems
- Strategic Initiative 3: Partner with other U.S. government departments and agencies and the private sector to enable a whole-of-government Cybersecurity strategy
- Strategic Initiative 4: Build robust relationships with U.S. allies and international partners to strengthen collective cybersecurity
- Strategic Initiative 5: Leverage the nation’s ingenuity through an exceptional cyber workforce and rapid technological innovation
National Strategic Cyberspace Initiative
The National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace identifies three strategic objectives:
- Prevent cyber attacks against America’s critical infrastructures;
- Reduce national vulnerability to cyber attacks
- Minimize damage and recovery time from cyber attacks that do occur.
What is Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the practice of keeping digital attacks from taking down important systems and sensitive information. Cybersecurity measures are also known as information technology (IT) security. They are meant to protect networked systems and applications from threats from inside or outside an organization.
Definition Cybersecurity: “Prevention of damage to, protection of, and restoration of computers, electronic communications systems, electronic communications services, wire communication, and electronic communication, including information contained therein, to ensure its availability, integrity, authentication, confidentiality, and nonrepudiation”. DoD Instruction 8500.01
What are the Cybersecurity Levels
Cyberspace can be viewed as three layers (physical, logical, and social) comprising five components (geographic, physical network, logical network, cyber persona, and persona).
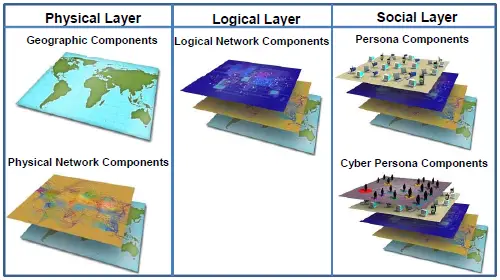
Physical:
The physical layer includes the geographic component and the physical network component. The geographic component is the physical location of elements of the network. While geopolitical boundaries can easily be crossed in cyberspace at a rate approaching the speed of light, there is still a physical aspect tied to the other domains. The physical network component includes all the hardware and infrastructure (wired, wireless, and optical) that supports the network and the physical connectors (wires, cables, radio frequency, routers, servers, and computers). [2]
Logical:
The logical layer contains the logical network component, which is technical and consists of the logical connections that exist between network nodes. Nodes are any devices connected to a computer network. Nodes can be computers, personal digital assistants, cell phones, or various other network appliances. On an Internet protocol (IP) network, a node is any device with an IP address. [2]
Social:
The social layer comprises the human and cognitive aspects, including the cyber persona and persona components. The cyber persona component includes a person’s identification or persona on the network (e-mail address, computer IP address, cell phone number, and others). The persona component consists of the people actually on the network. An individual can have multiple cyber personas (for example, different e-mail accounts on different computers), and a single cyber persona can have multiple users. [2]
“Cybersecurity threats represent one of the most serious national security, public safety, and economic challenges we face as a nation.” – 2010 National Security Strategy
Where Did the Name Cyberspace Come From
William Gibson first used the term “cyberspace” in his 1984 book, Neuromancer. In later years, Gibson called the phrase “evocative and ultimately worthless,” criticizing it. However, the phrase is still frequently used to refer to any resource or feature that is connected to the Internet. The phrase often refers to various virtual interfaces that produce digital realities.
AcqLinks and References:
- [1] DoD Strategy for Operating in Cyberspace, July 2011
- [2] Cyberspace Operations Concept Capability Plan 2016-2028, 20 Feb 2010
- DoD Cyberspace Policy Report A “Report to Congress Pursuant to the NDA Act” – Nov 2011
- GAO 11-75 Report DoD Cyber Efforts ”DOD Faces Challenges In Its Cyber Activities” – July 2011
- The National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace Feb 2003
- Website: DoD Cyber Strategy
Updated: 2/21/2024
Rank: G11
