 Cybersecurity falls under Information Operations (IO) and is used to protect and defend information and information systems. It’s the practice of keeping digital attacks from taking down important systems and sensitive information. They are meant to protect networked systems and applications from threats from inside or outside an organization.
Cybersecurity falls under Information Operations (IO) and is used to protect and defend information and information systems. It’s the practice of keeping digital attacks from taking down important systems and sensitive information. They are meant to protect networked systems and applications from threats from inside or outside an organization.
Definition: “Prevention of damage to, protection of, and restoration of computers, electronic communications systems, electronic communications services, wire communication, and electronic communication, including information contained therein, to ensure its availability, integrity, authentication, confidentiality, and nonrepudiation”. DoD Instruction 8500.01
Guide: PM Guidebook for Integrating Cybersecurity RMF into System Acquisition Lifecycle – Sep 2015
What is Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the practice of keeping digital attacks from taking down important systems and sensitive information. Cybersecurity measures are also known as information technology (IT) security. They are meant to protect networked systems and applications from threats from inside or outside an organization.
What are the Cybersecurity Levels
Cyberspace can be viewed as three layers (physical, logical, and social) made up of five components (geographic, physical network, logical network, cyber persona, and persona).
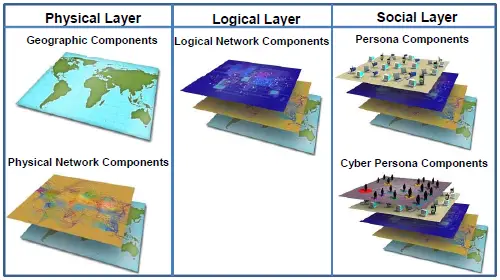
Physical:
The physical layer includes the geographic component and the physical network component. The geographic component is the physical location of elements of the network. While geopolitical boundaries can easily be crossed in cyberspace at a rate approaching the speed of light, there is still a physical aspect tied to the other domains. The physical network component includes all the hardware and infrastructure (wired, wireless, and optical) that supports the network and the physical connectors (wires, cables, radio frequency, routers, servers, and computers). [2]
Logical:
The logical layer contains the logical network component, which is technical and consists of the logical connections that exist between network nodes. Nodes are any devices connected to a computer network. Nodes can be computers, personal digital assistants, cell phones, or various other network appliances. On an Internet protocol (IP) network, a node is any device with an IP address. [2]
Social:
The social layer comprises the human and cognitive aspects, including the cyber persona and persona components. The cyber persona component includes a person’s identification or persona on the network (e-mail address, computer IP address, cell phone number, and others). The persona component consists of the people actually on the network. An individual can have multiple cyber personas (for example, different e-mail accounts on different computers) and a single cyber persona can have multiple users. [2]
“Cybersecurity threats represent one of the most serious national security, public safety, and economic challenges we face as a nation.” – 2010 National Security Strategy
DoD Strategic Cyberspace Initiative
Below is a list of the five (5) DoD Strategic Initiatives for Cyberspace: [1]
- Strategic Initiative 1: Treat cyberspace as an operational domain to organize, train, and equip so that DoD can take full advantage of cyberspace’s potential
- Strategic Initiative 2: Employ new defense operating concepts to protect DoD networks and systems
- Strategic Initiative 3: Partner with other U.S. government departments and agencies and the private sector to enable a whole-of-government Cybersecurity strategy
- Strategic Initiative 4: Build robust relationships with U.S. allies and international partners to strengthen collective cybersecurity
- Strategic Initiative 5: Leverage the nation’s ingenuity through an exceptional cyber workforce and rapid technological innovation
National Strategic Cyberspace Initiative
The National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace identifies three strategic objectives:
- Prevent cyber attacks against America’s critical infrastructures;
- Reduce national vulnerability to cyber attacks
- Minimize damage and recovery time from cyber attacks that do occur.
AcqNotes:
- Cybersecurity replaces the term information assurance
AcqLinks and References:
- Defense Acquisition Guidebook (DAG)
- DoD 8570.01-m “Information Assurance Workforce Improvement Program” – 10 Nov 15
- DoD Directive 8140.01 “Cyberspace Workforce Management” – 31 July 17
- DoD Instruction 8500.01 Cybersecurity – 14 Mar 2014
- DoD Instruction 8510.01 Risk Management Framework (RMF) for DoD Information Technology (IT) – 24 May 2016
- Old: DoD Instruction 8510.01 Risk Management Framework (RMF) for DoD Information Technology (IT) – 12 Mar 2014
- Guide: USAF System Security Engineering Cyber Guidebook v4.0 – 29 July 2021
- Guide: PM Guidebook for Integrating Cybersecurity RMF into System Acquisition Lifecycle – Sep 2015
- Guide: DoD CIO Cybersecurity Strategy Outline and Guidance – 10 Nov 15
- Cybersecurity and Acquisition Lifecycle Integration Tool (CALIT) Ver 2.02
- Cybersecurity Policy Chart – 27 Oct 2015
- Presentation: CMMC “Securing the DoD Supply Chain Overview – Nov 2019
- Website: Defense Information Agency (DISA)
- Website: DoD ISAE
Updated: 11/25/2021
