Electronic Warfare (EW) refers to any action involving the use of the electromagnetic spectrum or directed energy to control the spectrum, attack an enemy, or impede enemy assaults via the spectrum. The purpose of electronic warfare is to deny the opponent the advantage of, and ensure friendly unimpeded access to, the EM spectrum. EW is waged throughout the electromagnetic spectrum to secure and maintain effective control and use through the integration of detection, denial, deception, disruption, and destruction. EW can be applied from air, sea, land, and space by manned and unmanned systems, and can target communication, radar, or other services.
Electronic Warfare (EW) Subdivisions
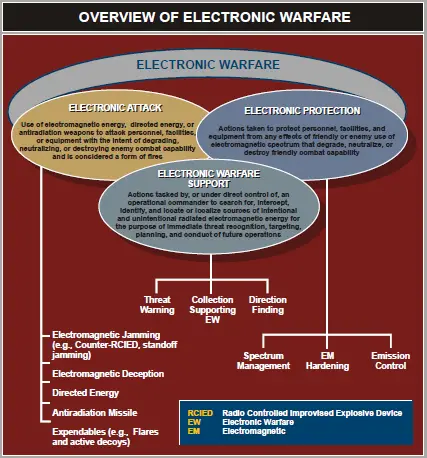
EW includes three (3) major subdivisions: [1]
- Electronic Attack (EA): involves the use of EM energy, directed energy, or anti-radiation weapons to attack personnel, facilities, or equipment with the intent of degrading, neutralizing, or destroying enemy combat capability.
- Electronic Protection (EP): involves actions taken to protect personnel, facilities, and equipment from any effects of friendly or enemy use of the electromagnetic spectrum that degrade, neutralize, or destroy friendly combat capability.
- Electronic Warfare Support (ES): involves the search for, intercept, identify, and locate or localize sources of intentional and unintentional radiated EM energy for the purpose of immediate threat recognition, targeting, planning, and conduct of future operations.
Electronic Warfare (EW) in Information Operations (IO)
EW contributes to the success of Information Operations (IO) by using offensive and defensive tactics and techniques in a variety of combinations to shape, disrupt, and exploit adversarial use of the EM spectrum while protecting friendly freedom of action in that spectrum. Expanding reliance on the EM spectrum increases both the potential and the challenges of EW in IO. All of the core, supporting, and related IO capabilities either directly use. Activities used in EW include: [2]
- Electro optical-infrared and radio frequency countermeasures;
- EM compatibility and deception;
- EM hardening, interference, intrusion, and jamming;
- Electronic masking, probing, reconnaissance, and intelligence;
- Electronics security;
- EW reprogramming;
- Emission control;
- Spectrum management;
- and wartime reserve modes

- [1] Joint Publication 3-13.01 “Electronic Warfare” – 25 Jan 07
- [2] Air Force Doctrine Document 2-5.1 “Electronic Warfare”- 5 Nov 02
- CRS “Information Operations, Electronic Warfare, and Cyberwar” – 20 Mar 07
Updated: 7/30/2021