Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) is a visual representation technique that depicts the activities involved in a project. It is a method of constructing a project schedule network diagram that uses boxes/nodes to represent activities and connects them with arrows that show the dependencies. It’s also sometimes called the activity-on-node (AON) method.
Purpose of Precedence Diagram Method (PDM)
The purpose of the Precedence Diagram Method is to produce a more accurate scheduling network diagram. The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and Critical Path Method (CPM) techniques are essentially limited to “finish-start” relationships (i.e., activity B cannot start until activity A is completed). PDM was developed after the PERT/CPM techniques, and its function is to permit a more accurate depiction of relationships among various activities.
Key Takeaways of Using the Precedence Diagram Method (PDM)
The Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) is a way to schedule activities in a project by showing them on a scheduled network diagram. It is a way to show how activities relate to each other logically and to make a project schedule network diagram. Some important things to remember about using the PDM are:
- PDM is a useful tool for planning and scheduling projects because it makes it easy to see how different tasks relate to each other and in what order they should be done.
- PDM is based on the idea of priority, meaning that some things must be done before others can start. This is shown in the diagram by showing how activities depend on each other.
- PDM can be used to make a project schedule that shows when each task will begin and end. This helps find the project’s critical path, which is the order of tasks that determines how long the whole project will take.
- PDM can help find problems or bottlenecks in a project’s schedule and make plans to deal with them.
- PDM can be used with other tools and techniques for project management, like the critical path method, to help plan and manage projects better.
How is the Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) Depicted
The Precedence Diagram is depicted by a chart with nodes and their relationships. An arrow connects two nodes to represent an active relationship. It’s also called a nodal diagram or network diagram.
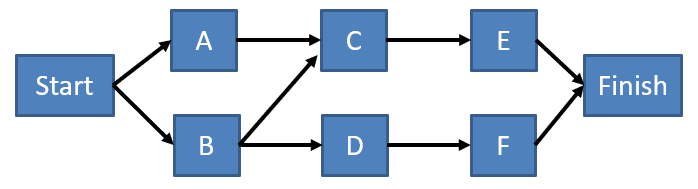
- Precedence Diagram Method (PDM)
Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) Benefits
There are a lot of benefits that can be obtained by using the PDM. These are:
- Highlights relationships and dependencies among activities to ensure planning efficiency.
- Identifies possible missing activities.
- Helps identify critical activities to ensure better planning.
- Helps develop the overall project schedule.
- Good communication tool for project team members.
The Four Precedence Diagram Methods (PDM)
The PDM has four ways of developing the diagram. These methods are:
- Finish-Start: In this dependency, an activity cannot start before a previous activity has ended. This is the most commonly used dependency.
- Start-Start: In this dependency, there is a defined relationship between the start of activities.
- Finish-Finish: In this dependency, there is a defined relationship between the end dates of activities.
- Start-Finish: In this dependency, there is a defined relationship between the start of one activity and the end date of a successor activity. This dependency is rarely used.
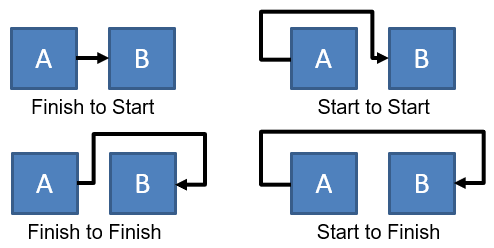
- Precedence Diagram Method Dependencies
Steps to Developing a Precedence Diagram
- Step 1: Break your Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) into activity levels.
- Step 2: List all activities and their sequences in a table.
- Step 3: Add relationships and dependencies to each activity in the table.
- Step 4: Draw the diagram.
Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) Dependency Levels
- Mandatory Dependency: known as hard logic is an integral part of the work. Example: Activity A must be completed before activity B can start.
- Discretionary Dependency: preferential or soft logic. Example: Dependency is controlled by the project team and can be changed.
- External Dependency: Comes from outside of the project. Example: Laws and Regulations or waiting for government funding to begin the project.
- Internal Dependency: involves a precedence relationship between project activities. Example: Can’t start until the previous internal project is completed.
How a Precedence Diagram Method (PDM) Helps Program Managers
Network scheduling techniques provide Program Managers with a powerful tool for scheduling and controlling their programs/projects. In general, they permit the graphic portrayal of project activities and relationships among the activities. This provides the basis for determining the project’s critical path, predicting shortages, and identifying possible reallocation of resources to solve problems.
Through the use of readily available software, network schedules are fairly easy to update and rework, thus providing managers with current program/project status information and control over activities and schedules. [1]
AcqNotes Tutorial
AcqLinks and References:
- Defense System Management College “Scheduling Guide for Program Managers” – Oct 2001
- DoD “Integrated Master Plan and Integrated Master Schedule Preparation and User Guide” – 21 Oct 2005
- CDC “Project Scheduling Best Practices/Guide” – 30 Jun 2007
- GAO 12-120G “Schedule Assessment Guide: Best Practices for Project Schedule” – May 2012
Updated: 2/2/2024
Rank: G2.9
