Middle Tier Acquisition (MTA) is a rapid acquisition interim approach that focuses on delivering capability in a period of 2-5 years with rapid prototypes and rapid fielding with proven technology. The approach is part of the Adaptive Acquisition Framework.
Definition: The Middle Tier of Acquisition pathway is used to rapidly develop fieldable prototypes within an acquisition program to demonstrate new capabilities and/or rapidly field production quantities of systems with proven technologies that require minimal development. [1]
Adaptive Acquisition Framework and Middle Tier Acquisitions (MTA)
The Adaptive Acquisition Framework (AAF) provides six different acquisition strategy pathways for Program Managers (PM) to utilize in developing a product or system with MTA as one of them. The framework six (6) acquisition pathways are.
- Urgent Capability Acquisition
- Middle Tier of Acquisition
- Major Capability Acquisition
- Software Acquisition
- Defense Business System
- Acquisition of Services
Middle Tier Acquisition (MTA) Purpose
The purpose of the MTA pathway is intended to fill a gap in the Defense Acquisition System (DAS) for those capabilities that have a level of maturity to allow them to be rapidly prototyped within an acquisition program or fielded, within 5 years of MTA program start. The MTA pathway may be used to accelerate capability maturation before transitioning to another acquisition pathway or may be used to minimally develop a capability before rapidly fielding. [1]
Middle Tier Acquisition (MTA) Approach
The approach consists of utilizing two (2) acquisition pathways: (1) Rapid Prototyping and (2) Rapid Fielding. It does this by streamlining the testing and deployment of prototypes or upgrading existing systems with already proven technology.
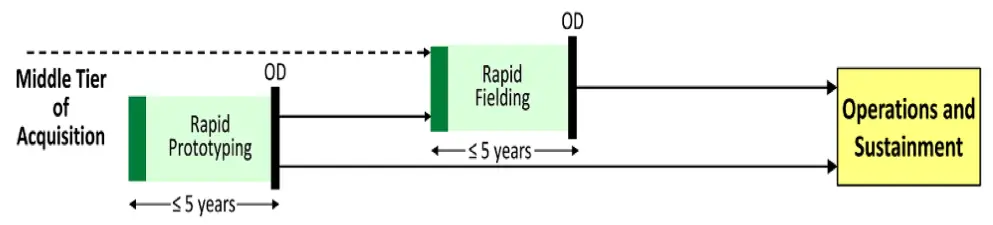
Figure: Middle Tier Acquisition Approach
Instruction: DoD Instruction 5000.80 “Operations of the MTA”
(1) Rapid Prototyping
Use innovative technology to rapidly develop fieldable prototypes to demonstrate new capabilities, meet emerging military needs. The objectives are:
- Field a prototype that can be demonstrated in an operational environment
- Provide for residual operational capability within 5 years of an approved requirement
(2) Rapid Fielding
Use proven technologies to field production quantities of new or upgraded systems with minimal development required. The objectives are:
- Begin production within 6 months
- Complete fielding within 5 years of an approved requirement
Middle Tier Acquisition Comparison
The Middle Tier Acquisition (MTA) pathway’s (Rapid Prototyping & Rapid Fielding) focuses on achieving three unique advantages compared to traditional and other acquisition pathways. These (3) three advantages are:
- Reduction of Risk and Cost Savings
- Creates new business opportunities and paves the path for more innovative solutions
- Acceleration of capability development
Middle Tier Acquisition (MTA) Authority
The interim approach was granted by Congress in the FY16 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) Section 804 and is not be subject to the Joint Capabilities Integration Development System (JCIDS) and DOD Directive 5000.01 “Defense Acquisition System”.
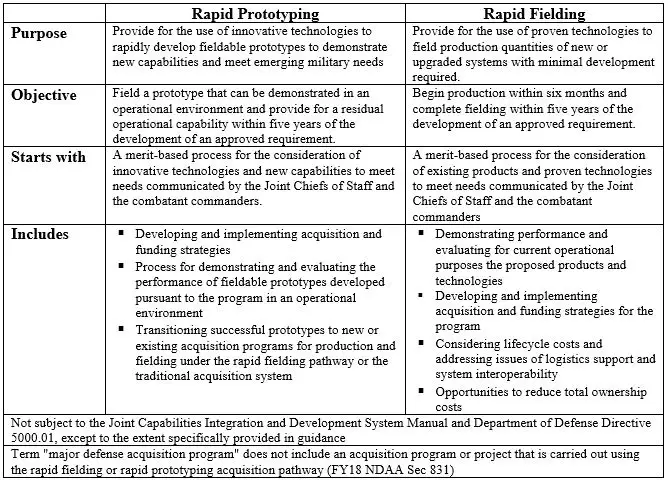 Table: Summary of NDAA 2016, Section 804 Statutory Language
Table: Summary of NDAA 2016, Section 804 Statutory Language
Middle Tier Acquisition (MTA) Funding
- Organizations must make use of their existing funding consistent with the purpose for which the funds were appropriated.
- Interim authority does not cover the establishment of Rapid Prototyping Fund
- Rapid Prototyping Fund will be authorized when approved by organizations responsible for those authorities.
AcqNotes Tutorial
AcqLinks and References:
- [1] DoD Instruction 5000.80 “Operations of the Middle Tier of Acquisitions (MTA)
- FY16 NDAA Section 804 “Middle Tier Acquisition”
- Presentation: DAU Middle Tier Acquisition Interim Authority & Guidance
- Memo: USD(AS) Memo MTA (Rapid Prototyping-Rapid Fielding) Interim Governance 2 – 20 Mar 2019
- Memo: OSD Middle Tier of Acquisition Interim Authority and Guidance – 16 Apr 2018.
- Memo: Air Force 7 Steps for Incorporating Rapid Prototyping into Acquisition
- Memo: Air Force Guidance Memorandum for Rapid Acquisition Activities – 13 June 2018
- Memo: Navy Middle Tier Acquisition and Acquisition Agility Guidance – 24 April 2018
Updated: 9/25/2022
Rank: G2
